-
Excited-State Symmetry Breaking in a Quadrupolar Molecule Visualized in Time and Space
B. Dereka, A. Rosspeintner, R. Stezycki, C. Ruckebusch, D.T. Gryko and E. Vauthey
The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 8 (2017), p6029-6034


DOI:10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b02944 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF | Supporting Info
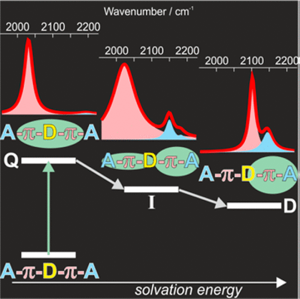
The influence of the length of the push–pull branches of quadrupolar molecules on their excited-state symmetry breaking was investigated using ultrafast time-resolved IR spectroscopy. For this, the excited-state dynamics of an A-π-D-π-A molecule was compared with those of an ADA analogue, where the same electron donor (D) and acceptor (A) subunits are directly linked without a phenylethynyl π-spacer. The spatial distribution of the excitation was visualized in real time by monitoring C≡C and C≡N vibrational modes localized in the spacer and acceptor units, respectively. In nonpolar solvents, the excited state is quadrupolar and the excitation is localized on the π-D-π center. In medium polarity solvents, the excitation spreads over the entire molecule but is no longer symmetric. Finally, in the most polar solvents, the excitation localizes on a single D-π-A branch, contrary to the ADA analogue where symmetry breaking is only partial.